C++ While Loop Control Structure
Introduction
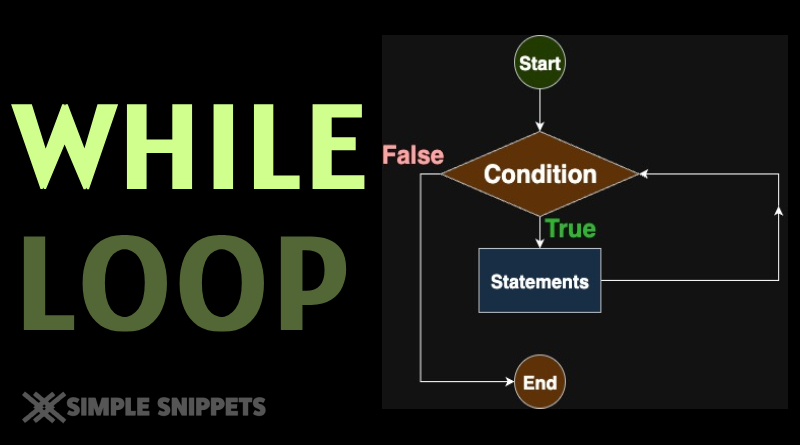
The while loop in C++ is used when the number of iterations is not known in advance. It keeps executing a block of code as long as the given condition is true. This makes it ideal for cases where you want to loop until a specific event occurs (like user input, reaching a target, or waiting for a condition).
Syntax
while (condition) {
// statements
}- condition: evaluated before each iteration.
- If condition is true → body executes.
- If condition is false → loop stops immediately.
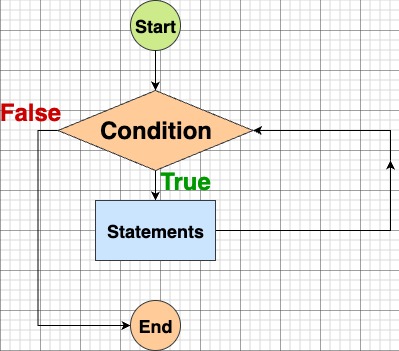
Working of While Loop
- Test the condition.
- If true → run loop body → go back to step 1.
- If false → exit loop.
Example: Print numbers 1 to 5 using While Loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
cout << i << " ";
i++;
}
return 0;
}Output:
1 2 3 4 5Key Points
- Entry-controlled loop → condition is checked first, so loop may run 0 times if condition is false initially.
- Ideal when the stopping condition is not known in advance.
Common Uses
- Reading input until a sentinel value (e.g., until user enters 0).
- Loops where iterations depend on calculations instead of fixed count.
Tips
- Always ensure your condition eventually becomes false (otherwise infinite loop).
- Use
breakcarefully if you need to exit earlier.