C++ Switch Case Control Structure
Introduction
In this tutorial, we will learn about the switch case control structure in C++.
A switch statement allows a variable to be tested against multiple constant values. Each value is called a case, and the variable being checked is compared to each case until a match is found.
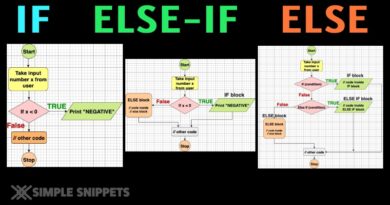
Switch case is often used as a cleaner alternative to writing multiple if-else-if statements when checking a variable against many possible values.
Key Points about Switch Case in C++
- The expression inside
switch()must be of integral type (e.g.,int,char,enum). - Floating-point values are not allowed.
- Each case must have a constant value (variable values are not allowed).
breakis used to exit the switch block after a case executes. Withoutbreak, execution will fall through to the next case.- The default case is optional but useful when no case matches.
Syntax of Switch Case in C++
switch(expression) {
case constant1:
// statements
break; // optional
case constant2:
// statements
break; // optional
// you can have multiple cases
default:
// statements (optional)
}Flowchart of Switch Case Statement
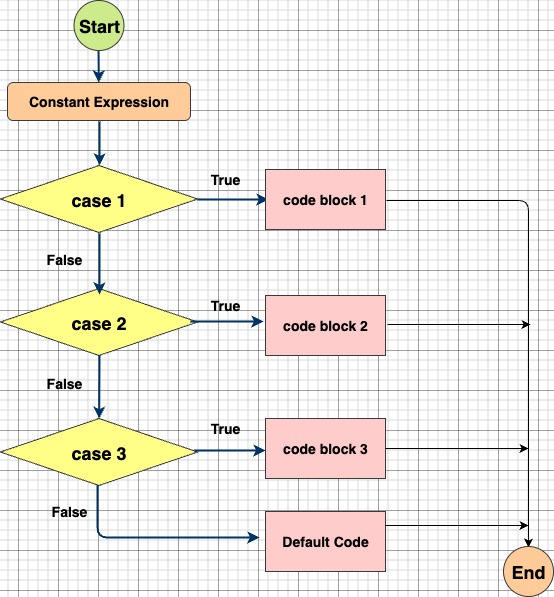
Example Program: Print Day of the Week
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num;
cout << "Enter a number between 1 and 7: ";
cin >> num;
switch(num) {
case 1:
cout << "Monday";
break;
case 2:
cout << "Tuesday";
break;
case 3:
cout << "Wednesday";
break;
case 4:
cout << "Thursday";
break;
case 5:
cout << "Friday";
break;
case 6:
cout << "Saturday";
break;
case 7:
cout << "Sunday";
break;
default:
cout << "Invalid Input";
}
return 0;
}Output
Enter a number between 1 and 7: 3
WednesdayExplanation of the Example
- The user enters a number (
1–7). - The
switch(num)checks the entered number against each case. - If
num == 3, the output is"Wednesday". - The
breakstatement ensures the program exits the switch once a match is found. - If no case matches, the
defaultcase runs.
Advantages of Switch Case over If-Else
✅ Cleaner and more readable when checking multiple values.
✅ Better performance in some cases since the compiler optimizes switch statements.
✅ Avoids writing long chains of if-else-if conditions.
Final Notes
- Use switch-case when dealing with fixed, known values.
- Use if-else when working with ranges or complex conditions (
>,<,==, etc.).