C++ Multidimensional Arrays – 2D Arrays (With Examples)
Introduction
In this tutorial, we will learn about multidimensional arrays in C++, with a focus on 2D arrays (two-dimensional arrays).
A multidimensional array is essentially an array of arrays. Among them, 2D arrays are the simplest and most commonly used. They are often used to represent data in a tabular format (rows and columns) — just like a matrix.
👉 If you are new to arrays, you may first check out our guide on C++ Arrays before continuing.
General Declaration Syntax
The syntax for declaring a multidimensional array is:
type arrayName[size1][size2]...[sizeN];Example of a 3D array declaration:
int threeD[5][10][4];Two-Dimensional Arrays (2D Arrays)
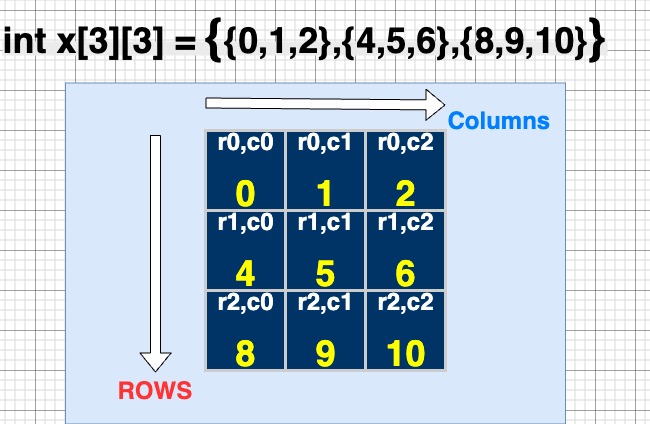
A 2D array in C++ can be visualized as a table with rows and columns.
Each element of the array can be accessed using two indices:
i→ row indexj→ column index
Syntax:
type arrayName[rows][columns];For example:
int matrix[3][3];This creates a 3×3 table (3 rows and 3 columns).
Declaring and Initializing 2D Arrays
There are multiple ways to initialize 2D arrays in C++:
Method 1: Row-by-Row Initialization
int Arr[3][3] = {
{0, 1, 2}, // row 0
{4, 5, 6}, // row 1
{8, 9, 10} // row 2
};Method 2: Inline Initialization
int Arr[3][3] = {0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10};Method 3: Single Element Assignment
int Arr[3][3];
Arr[0][1] = 50; // Sets element at row 0, column 1 to 50Accessing 2D Array Elements
You can access elements using their row and column indices:
int x = Arr[0][1]; // Access element at row 0, column 1Traversing the Entire 2D Array
We generally use nested for loops:
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
cout << Arr[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}Example Program: Input and Output of a 2D Array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int A[2][2];
// Taking input from the user
cout << "Enter values of 2-D array A: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cin >> A[i][j];
}
}
// Printing the array
cout << "Values of 2-D array A: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cout << A[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}Sample Input:
1 2
3 4Sample Output:
Values of 2-D array A:
1 2
3 4Visual Representation of a 2D Array
Imagine this 2D array:
int A[2][2] = { {1, 2}, {3, 4} };It looks like this:
| Row/Col | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 | 4 |
👉 Each element is accessed as A[row][column].
Applications of 2D Arrays
2D arrays are widely used in:
- Matrices and mathematical computations
- Game boards (like Chess, Sudoku, Tic-Tac-Toe)
- Image processing (pixels stored in rows and columns)
- Tabular data storage (like student marks, sales data, etc.)
Key Takeaways
- A 2D array is like a table with rows and columns.
- Elements are accessed with two indices →
Arr[i][j]. - You can initialize 2D arrays in multiple ways.
- Nested loops are commonly used to traverse 2D arrays.