C++ For Loop Control Structure
Introduction
In programming, loops let you repeat tasks efficiently. In C++, the for loop is used when you know in advance how many times you want the loop to run (or can express it numerically). This makes for loops ideal for fixed-count iterations, arrays, traversals, and more.
Syntax of the For Loop in C++
for (init; condition; increment) {
// statements to repeat
}- init: executed once at the start (often used to initialize loop counter).
- condition: evaluated before every iteration; if true, loop body executes; if false, loop ends.
- increment: executed at the end of each iteration (often used to update loop counter).
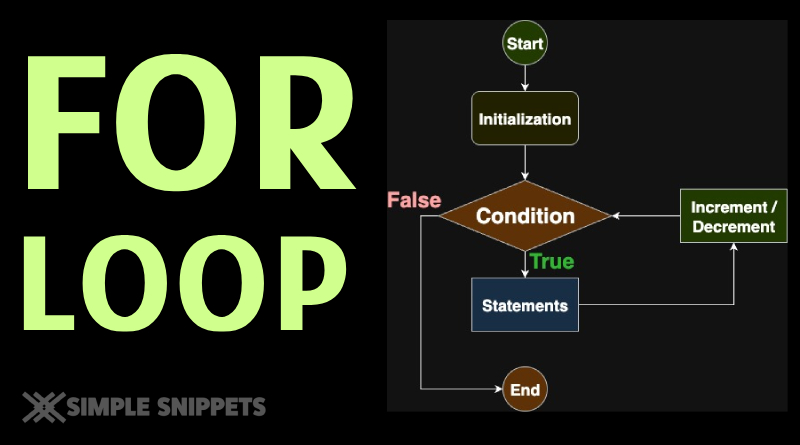
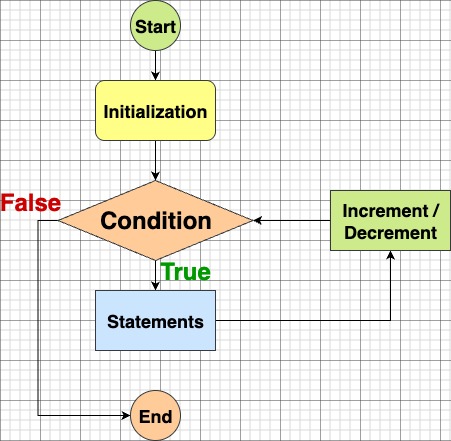
Working / Flow of the For Loop
initruns once.- Test
condition.- If true → execute loop body → then
increment→ back to step 2. - If false → exit loop and continue after the loop.
- If true → execute loop body → then
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 5;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// Printing 5’s multiplication table
cout << x << " x " << i << " = " << (x * i) << endl;
}
return 0;
}Example: Multiplication Table using For Loop
Output:
5 x 1 = 5
5 x 2 = 10
5 x 3 = 15
…
5 x 10 = 50 Explanation
- The loop starts with
i = 1. - Checks
i <= 10→ true, enters body. - Prints
5 x i = result. - After printing,
i++incrementsi. - Loops until
i = 11, wherei <= 10is false → exit loop.
Variations & Advanced Uses
- Multiple init or increment expressions:
for (int i = 0, j = 10; i < j; i++, j--) { // do something } - Omitting parts (rarely recommended):
You can omitinit,condition, orincrement(but then you must handle them inside the loop to avoid infinite loops).int i = 0; for ( ; i < 5; ) { cout << i << " "; i++; } - Infinite loop using for:
for ( ;; ) { // runs forever until break or return }
When to Use For vs While vs Do-While
- Use for loop when you know (or can calculate) how many times you need to loop.
- Use while loop when the termination condition depends on external constraints or inputs.
- Use do-while when you always want the loop body to execute at least once.
Tips & Best Practices
- Always use braces
{}even for single-line bodies — avoids errors when you extend the loop later. - Avoid modifying the loop variable inside the body in unexpected ways — keep
incrementclear. - Don’t let loops run too long (watch out for off-by-one errors).
- Use
breakorcontinuecarefully inside for loops (you may refer to jump statements post).