C++ Arrays – Definition, Syntax, Initialization, and Examples
Introduction to Arrays in C++
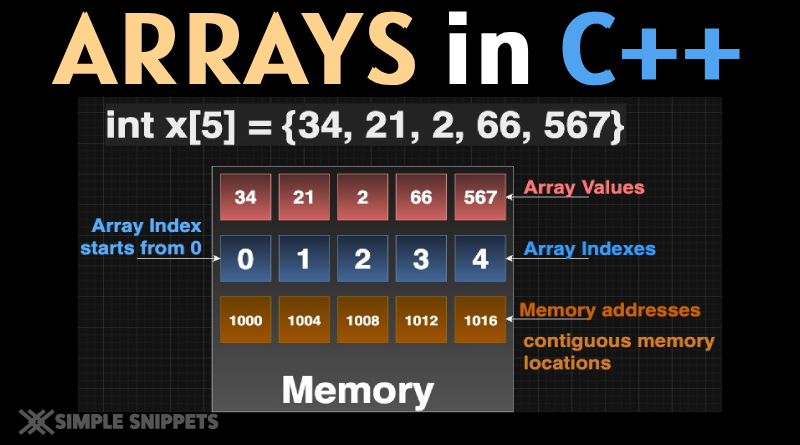
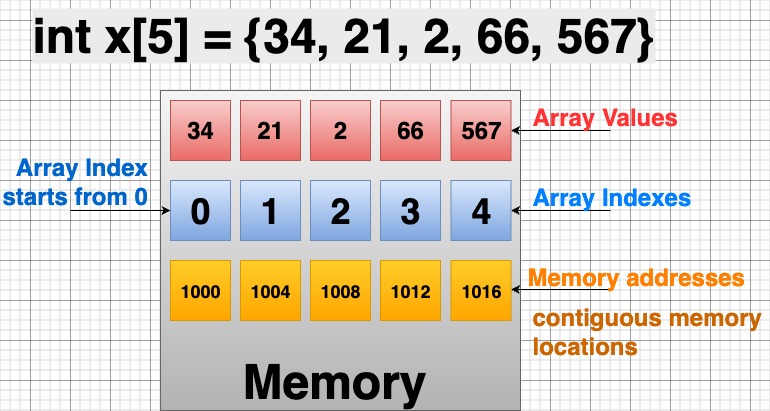
In C++ programming, an array is a collection of elements of the same data type, stored in contiguous memory locations. Each element can be accessed using an index.
👉 Example:
Instead of creating 100 different variables to store the ages of 100 people, you can create a single integer array of size 100:
int Age[100];Here, all 100 values are stored in continuous memory, where:
- The lowest memory address corresponds to
Age[0]. - The highest memory address corresponds to
Age[99].
✅ This makes arrays efficient and easier to use.
Array Diagram –
Declaring Arrays in C++
The basic syntax is:
type arrayName[arraySize];type→ Data type of elements (int, float, char, etc.)arrayName→ Name of the arrayarraySize→ Must be an integer constant greater than 0
✅ Example:
double Arr[5]; // Array of 5 doubles
int marks[10]; // Array of 10 integers
char letters[26]; // Array of 26 charactersInitializing Arrays
You can initialize arrays in multiple ways:
1. Direct Initialization
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};2. Partial Initialization
If fewer elements are given, remaining ones are initialized to 0:
int numbers[5] = {10, 20}; // {10, 20, 0, 0, 0}3. Implicit Size
If the size is omitted, it is automatically determined:
int numbers[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // size = 54. Single Element Assignment
int marks[5];
marks[0] = 95; // Assigning value to first element
marks[4] = 88; // Assigning value to fifth element⚠️ Note: Array indices start from 0. So for an array of size n, valid indices range from 0 to n-1.
Accessing Array Elements
You can access elements using their index:
cout << marks[0]; // prints first element
cout << marks[4]; // prints fifth elementTo traverse all elements, loops are commonly used:
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
cout << marks[i] << endl;
}Example Program: Arrays in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Declaration & initialization
int arr[3] = {1, 2, 3};
double arr1[5];
arr1[0] = 1.456;
arr1[1] = 36.765;
char myarr[4];
myarr[0] = 'a';
// Taking input in array
int temp_arr[5];
cout << "Enter 5 integers:" << endl;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
cin >> temp_arr[i];
}
// Displaying array values
cout << "The values you entered are:" << endl;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
cout << temp_arr[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}📌 Sample Output:
Enter 5 integers:
10 20 30 40 50
The values you entered are:
10
20
30
40
50Key Points About Arrays
- Arrays always start with index 0.
- Size of the array must be fixed at declaration.
- Accessing out-of-bounds elements leads to undefined behavior.
- Arrays can be traversed easily with loops.
- Arrays are stored in contiguous memory blocks.
Conclusion
Arrays are a fundamental concept in C++ that make handling multiple values of the same type efficient and simple.
They form the foundation for advanced data structures like strings, matrices, and pointers.
👉 Next, you should explore Multi-Dimensional Arrays to learn how arrays can represent tables and matrices.